
Industrial Oven Buying Guide: Find Your Perfect Heat Treat Solution
Share
Why Industrial Ovens Are Essential for Modern Manufacturing
An industrial oven is a heated chamber designed for thermal processing applications like curing, drying, and baking components or final products. These powerful machines are cornerstones in industries ranging from food production and pharmaceuticals to aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
Common types include batch ovens for varied production, conveyor ovens for high-volume automation, and large walk-in ovens for oversized parts. Specialty models are also available for clean room, inert atmosphere, or Class A safety applications.
Unlike standard commercial ovens, industrial ovens feature robust construction, precise temperature control (often within 2°F accuracy), and the ability to handle continuous, demanding processes. They achieve this through forced convection, advanced insulation, and sophisticated control systems. Many large-scale bakeries, restaurants, and food manufacturers build their entire operation around a reliable industrial oven.
I'm Sean Kearney from Charbroilers.com, and with over a decade in the restaurant equipment industry, I've helped countless businesses find the right industrial oven solutions. My experience spans from compact benchtop units to massive walk-in systems, and I understand the critical role these machines play in both food production and manufacturing.
Explore more about industrial oven:
What is an Industrial Oven and How Does It Work?
Think of an industrial oven as the heavy-duty cousin of your kitchen oven. While a home oven bakes a roast, an industrial oven is curing car parts, drying electronics, or sterilizing medical equipment. Its primary function is heat treatment—subjecting materials to controlled high temperatures to change their physical or chemical properties.
Unlike furnaces that reach extreme temperatures for melting, industrial ovens operate with more precision, typically from just above ambient to around 1,400°F. They are also built more robustly than commercial ovens to handle continuous manufacturing and maintain tighter environmental controls.
The process relies on three heat transfer principles:
- Convection: The primary method, where fans circulate hot air to ensure uniform heating. Modern systems can maintain temperatures within 2°F.
- Conduction: Heat transfer through direct contact between the product and heated surfaces.
- Radiant Heat: Energy beamed directly onto the product, similar to how a toaster works. Infrared systems are a common example.
These key processes work together to create the precise thermal environment needed for proper material change.
Want to dive deeper into how these systems work in food service? Check out our guide on industrial convection ovens for more insights.
The Core Processes: Curing, Drying, and Baking
Every industrial oven specializes in three fundamental processes:
- Curing: Uses heat to trigger chemical reactions that create permanent changes, such as hardening a powder coating finish or solidifying polymers.
- Drying: Focuses on moisture removal, which is critical for evaporating water or solvents from parts to prevent corrosion and ensure proper coating adhesion.
- Baking: Combines curing and drying elements. This is essential in food production applications (bread, cookies) and for changing materials like clay and ceramics.
Key Components and How They Function
An industrial oven is a system of crucial components working in concert:
- Heat Source: Can be gas (natural gas or propane) for quick, economical heating; electric for precise, clean operation; or infrared for rapid, direct heating.
- Insulation: High-quality insulation is essential for maintaining stable temperatures and improving energy efficiency.
- Airflow Systems: Horizontal, vertical, or combination airflow patterns are designed to ensure even heat distribution across different product shapes and sizes.
- Control Systems: The "brain" of the oven, including temperature controllers for precision, timers for managing cycles, and fans for managing the oven's atmosphere.
Key Types of Industrial Ovens Explained
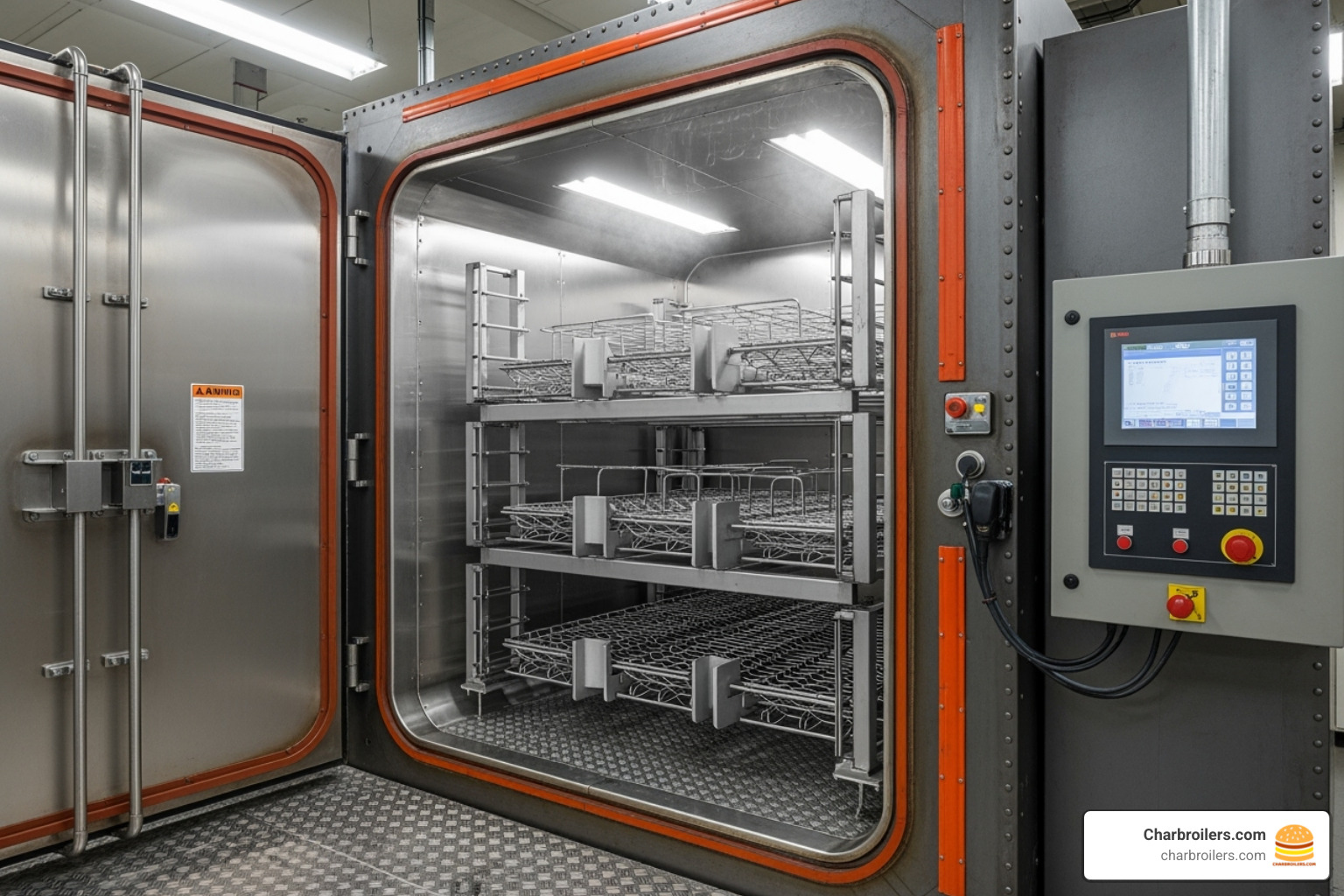

Just as a bakery wouldn't use a tiny countertop oven for hundreds of loaves, manufacturers must match their oven to their production needs. Each type of industrial oven is engineered for specific applications, from delicate electronics to massive aerospace components.
For those interested in diving deeper into the science behind these machines, scholarly articles on heat treatment offer fascinating insights into the engineering principles at work.
Batch Ovens vs. Continuous (Conveyor) Ovens
The biggest decision is choosing between batch processing or a continuous flow. It's like choosing between cooking a single large meal (batch) versus running a fast-food assembly line (continuous).
| Feature | Batch Ovens | Continuous (Conveyor) Ovens |
|---|---|---|
| Load Size | Inconsistent; small to very large | High volume; consistent product size |
| Production Vol. | Lower to medium volume; varied product mix | High volume; low product mix; automated processing |
| Loading Method | Manual loading, wheeled racks, forklift, crane | Automated conveyor belt, overhead conveyor, rotary |
| Flexibility | High; can handle different products/processes | Lower; optimized for specific, repetitive tasks |
| Footprint | Often smaller for equivalent batch size | Can be very long (heat tunnels) |
| Typical Use | Custom jobs, prototyping, varied production | Assembly lines, mass production |
Batch ovens are highly versatile, processing products in individual loads. This category includes smaller cabinet ovens and larger truck-in ovens that accommodate wheeled racks. They are ideal for operations with inconsistent load sizes or those that require the flexibility to switch between different products and processes.
Continuous ovens are built for speed and efficiency in high-volume production. Products move through heat tunnels on conveyor systems, making them perfect for integration into automated processing lines where products require identical, repeatable heat treatment.
For insights into how these industrial concepts translate to commercial kitchen applications, our guide on comparing commercial ovens provides valuable perspective.
Common Configurations and Their Specifications
Beyond batch versus continuous, industrial ovens come in various physical configurations:
- Walk-in Ovens: Room-sized units for massive parts or large quantities of smaller items, with temperatures often reaching up to 1200°F.
- Truck Loading Ovens: Designed for convenience, allowing entire wheeled racks to be rolled into the chamber. They are ideal for efficient product movement.
- Shelf Loading Ovens: A versatile mid-size option, often featuring non-tip shelves for safer and easier loading of individual parts.
- Bench Ovens: Compact, countertop units that deliver industrial-grade performance for laboratories or small-scale operations, with some models reaching 1000°F.
- Top-Loading Ovens: Feature upward-opening lids to allow for crane or hoist loading of heavy or bulky items.
Specialized Ovens for Demanding Environments
Some industries require precisely controlled environments beyond just heat:
- Clean Room Ovens: Used in semiconductor manufacturing and biotechnology, these ovens maintain strict control over airborne contamination and often feature silicone-free construction to prevent outgassing.
- Inert Atmosphere Ovens: Use non-reactive gases like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions during heating.
- Class A Safety Ovens: Designed to meet NFPA 86 standards for safely processing flammable solvents or volatile materials, incorporating features like explosion-resistant construction and improved ventilation.
How to Choose the Right Industrial Oven for Your Operation

Choosing the right industrial oven requires balancing your application, space, and budget. It's a significant investment, so consider these key factors:
- Application Needs: Are you curing, drying, baking, or sterilizing? Each process has unique temperature and time requirements.
- Production Volume: Do you need a flexible batch oven for varied jobs or a high-throughput conveyor system for mass production?
- Space Requirements: Measure your facility carefully to ensure the oven, whether it's a compact benchtop or a large walk-in model, will fit.
- Budgeting: Factor in the initial purchase price, installation, energy consumption, and maintenance costs.
- Customization: Decide if a standard model meets your needs or if you require an engineered-to-order solution for unique dimensions or processes.
Matching the Oven to Your Industrial Application
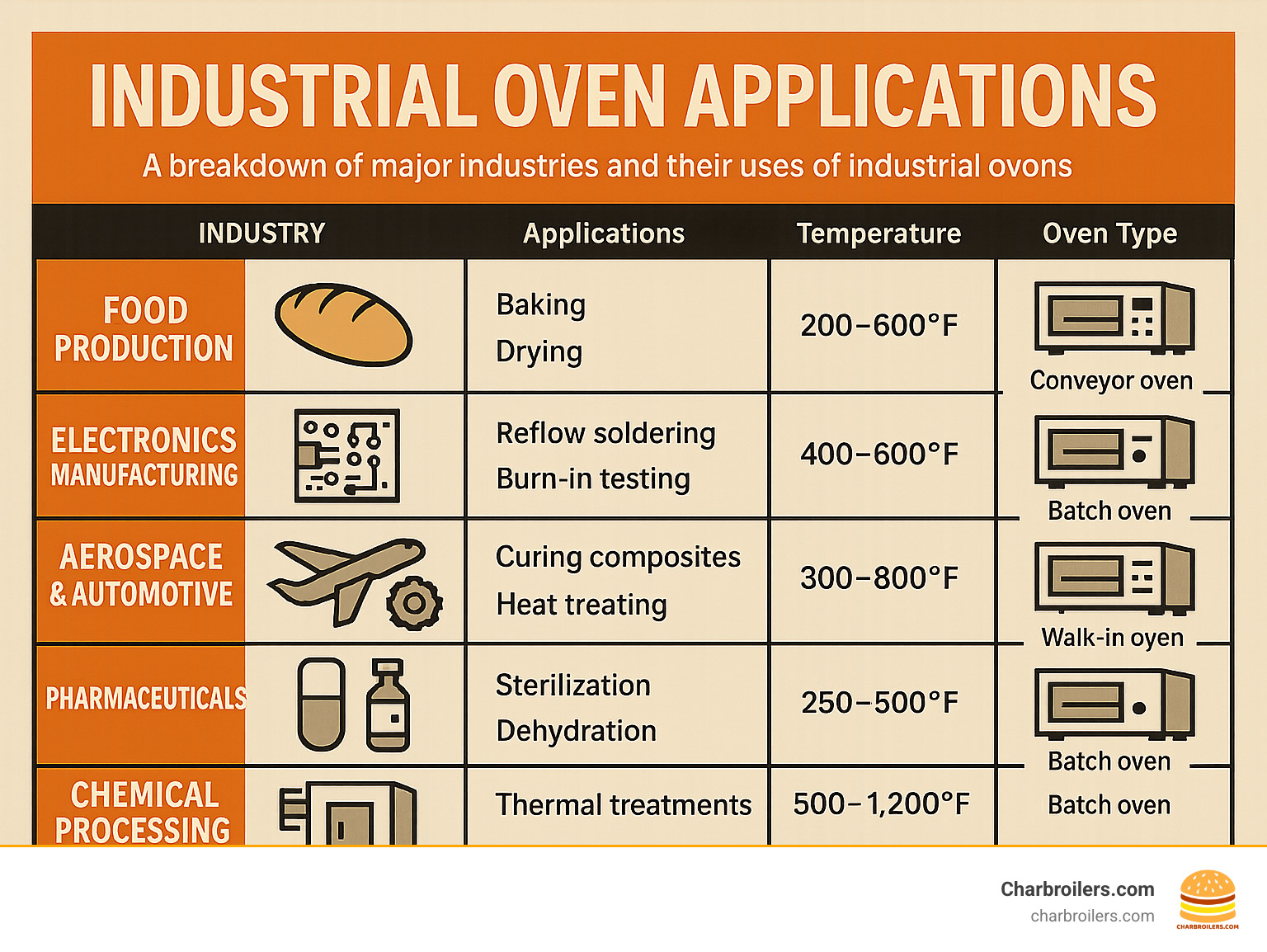
Industrial ovens are versatile workhorses across many sectors:
- Food Production: Used in large-volume bakeries for baking, in processing plants for drying fruits or jerky, and for roasting nuts and coffee beans.
- Electronics: Essential for precision tasks like reflow soldering on circuit boards and burn-in testing of components.
- Aerospace & Automotive: Critical for curing composites to create lightweight, strong materials and for heat treating parts to improve durability.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used for vital processes like sterilization of lab equipment and dehydration of active ingredients to ensure potency and shelf life.
Sizing and Capacity: From Benchtop to Walk-In Industrial Oven
Getting the size right is crucial for efficiency. Consider your interior workspace needs (WxDxH), ensuring enough room for parts and proper airflow. Also, calculate your load capacity based on batch size and required throughput (parts per hour). This will help you determine if you need a small laboratory oven (<10 ft³), a mid-size cabinet oven (<100 ft³), or a large walk-in oven (>100 ft³).
For businesses watching their budgets, we sometimes have information on Find local used oven deals that can provide excellent value.
Power Source and Temperature Control
Your choice between gas and electric power impacts both performance and operating costs.
- Gas Ovens: Offer faster heat-up times and can be more economical, but require proper ventilation for combustion by-products.
- Electric Ovens: Provide superior temperature uniformity and cleaner operation, making them ideal for sensitive processes, though they may have higher power requirements.
Look for excellent temperature uniformity to eliminate hot and cold spots. Ensure the oven's temperature range matches your process needs. Modern automated control systems offer incredible control precision, with temperature accuracy within 2°F and programmable ramp/soak profiles for complex heating cycles.
Best Practices for Industrial Oven Maintenance and Safety
An industrial oven is a major investment that requires proper care. Following best practices for maintenance and safety ensures its longevity, performance, efficiency, and operator safety. Preventative maintenance is the key to avoiding costly downtime.
For more in-depth information on keeping your industrial oven running smoothly, explore resources on Preventative Maintenance for Industrial Ovens.
A Practical Cleaning Schedule for Your Industrial Oven
Regular cleaning is fundamental to maintaining your industrial oven. A practical schedule includes:
- Daily: Brush out debris and wipe up any spills to prevent them from baking on.
- Weekly: Inspect door seals for wear and tear, and check that circulation fans are clean and operating correctly.
- Monthly: Perform a deep clean. Remove and soak racks, and thoroughly clean the interior walls with a suitable cleaner. Be careful to protect electrical components from moisture by using only a damp cloth on or near them.
Key Safety Standards and Operational Tips for Your Industrial Oven
Safety is non-negotiable when operating high-temperature equipment.
- NFPA 86 Compliance: If processing flammable materials, ensure your oven complies with NFPA 86 standards.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always use heat-resistant gloves, eye protection, and other appropriate PPE.
- Proper Ventilation: Maintain adequate ventilation to dissipate heat and remove fumes.
- Regular Inspections: Follow the manufacturer's schedule for inspecting wiring, heating elements, and safety interlocks.
- Lubrication: Regularly lubricate moving parts like door hinges or conveyor components to prevent wear.
- Operator Supervision: Never leave an industrial oven unattended during critical cycles or when processing volatile materials.
What to Look For in an Industrial Oven Manufacturer
When you're ready to invest in an industrial oven, choosing the right manufacturer is just as crucial as selecting the oven itself. Think of it this way: you're not just buying a piece of equipment, you're entering into a long-term partnership that could span decades.
The first thing to look for is experience. You want a manufacturer who's been around the block a few times and has seen it all. Companies that have weathered economic ups and downs, technological changes, and evolving industry standards bring invaluable wisdom to your project. They understand the nuances of different applications and can guide you away from common pitfalls.
Customization capabilities are absolutely essential in today's industrial landscape. While standard models work for many applications, chances are your operation has unique requirements. Maybe you need specific dimensions to fit your existing facility, or perhaps your process requires a special temperature profile. The best manufacturers accept these challenges and offer engineering support throughout the entire process.
Look for manufacturers who use modern design tools like 3D modeling. This technology allows you to visualize your oven before it's built, catch potential issues early, and ensure it integrates perfectly with your existing equipment. It's like having a crystal ball for your project.
After-sales service separates the great manufacturers from the merely good ones. Your relationship with them shouldn't end the moment your industrial oven arrives. Ask about installation support - will they help you get everything set up correctly? What about maintenance contracts to keep your oven running smoothly for years to come?
Don't forget about replacement parts. Even the best-built ovens need parts replaced eventually. A manufacturer who stocks genuine parts and can get them to you quickly will save you from costly downtime. Similarly, having access to knowledgeable technical support when you need troubleshooting help is invaluable.
Uniformity testing is where the rubber meets the road. Any manufacturer worth their salt will offer comprehensive testing to prove their oven maintains consistent temperatures throughout the workspace. This isn't just about meeting specifications - it's about ensuring your products come out perfect every time.
If possible, arrange for facility walkthroughs at the manufacturer's location. Seeing their operation tells you volumes about their quality control, attention to detail, and overall professionalism. It's one thing to talk about quality; it's another to see it in action.
The right manufacturer becomes your partner in success, helping you steer challenges and optimize your thermal processing operations for years to come.
Conclusion
Choosing the right industrial oven is a critical decision. By understanding the core principles of heat treatment and the various oven types, you can find the perfect solution for your needs.
The key is to match the oven to your specific application, whether it's curing, drying, or baking. Consider the type (batch vs. continuous), size (benchtop to walk-in), and power source (gas vs. electric) that best fit your production volume, facility space, and budget.
Prioritizing safety through proper maintenance and adherence to standards like NFPA 86 will protect your operators and your investment. A well-chosen and well-maintained industrial oven is a long-term asset that boosts efficiency and product quality for years to come.
At Charbroilers.com, we know that quality equipment is the backbone of any successful operation. While our expertise is in commercial kitchen equipment, the principles of selecting durable, efficient machinery are universal.
Ready to explore more essential equipment for your operation? Check out our comprehensive resource: Get our complete guide to commercial charbroilers and other essential kitchen equipment.

